In this blog, we'll use Ansible to set up Docker and a webserver in a Docker container.
There will be the following steps:
Install Ansible on the controller node.
Create inventory files & configure Ansible configuration files.
Create an Ansible playbook to install Docker in all the managed nodes.
Run Ansible Playbook.
Pre-requisite:
- Yum should be configured in the Managed Node.
**Step 1: ** Install Ansible in Controller Node
To install ansible using python3
pip3 install ansible
To install ansible in Linux:
yum install ansible
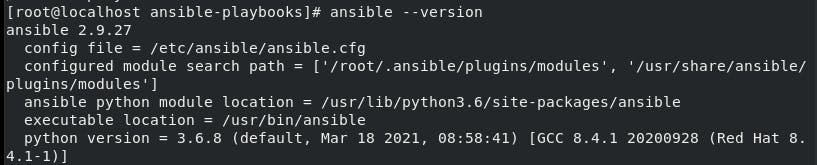
To check the version of ansible:
ansible --version
Step2: Create Inventory file & configure Ansible configuration file
We can add the Ip address of all the managed nodes. We can create an inventory file anywhere with a .txt extension but I am using the system by-default configuration file which is vim /etc/ansible/hosts
and adding the Ip address, Username, Password

- Now we can check the connectivity with Managed Node using the command
ansible all -m ping
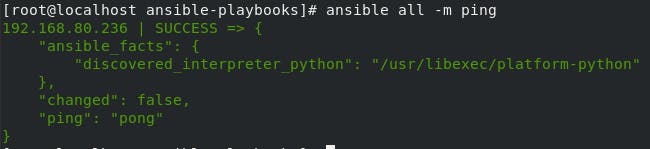
If it shows a message in green color that means there is connectivity and you will see the message ping pong.
Step 3: Create an Ansible Playbook to install Docker on all Managed Nodes.
**Ansible playbooks: ** Ansible playbooks is a YAML file that contains all the plays(tasks) ansible will perform. They are like a to-do list for Ansible that contains a list of tasks.
For doing our task we have to write Ansible Playbook that contains tasks.
The code in the playbook is as below:
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Docker repo
yum_repository:
name: docker
description: repo for docker
baseurl: "https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/7/x86_64/stable/"
gpgcheck: no
- name: installing docker
command: "yum install docker-ce --nobest -y"
- name: install python 3.6
package:
name: python36
state: present
- name: starting and enabling docker services
service:
name: docker
state: started
enabled: yes
- name: configure pip for docker
pip:
name: docker-py
- name: pull httpds docker iso
docker_image:
name: httpd
source: pull
- name: docker container
docker_container:
name: mywebserver
image: httpd
exposed_ports:
- 80
ports:
- 4444:80
volumes:
- /var/www/html/:/usr/local/apache2/htdocs
After successful running of the playbook, you can check the container whether it is launched successfully or not. Run the docker ps command to check the running container.
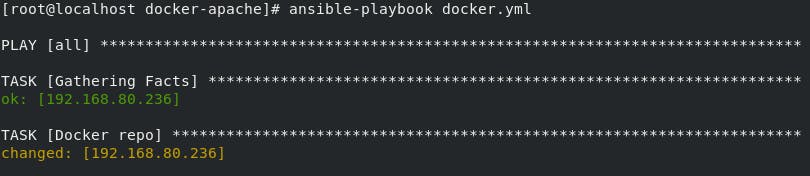
Step4: Run Ansible Playbook in Controller Node
To run Ansible Playbook we have ansible-playbook playbook_name command
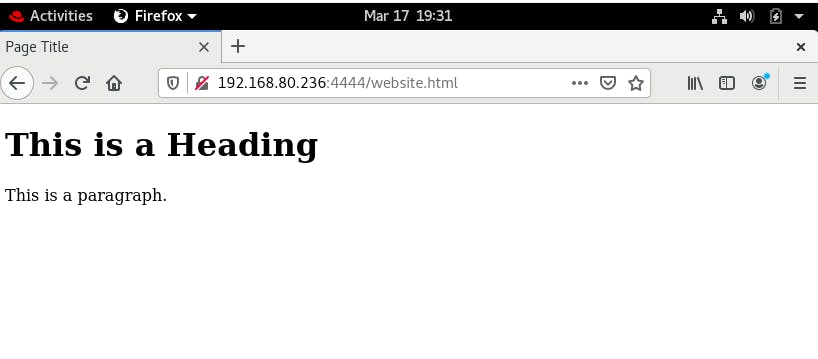
The output of the Website: URL = Managed_node_ip:portno
*** Thanks for reading! I hope you understood these concepts and learnt something. ***
If you have any queries feel free to reach out to me on Linkedin.